Discrete-time Control In Bilateral Teleoperation
Discrete-time control in bilateral teleoperation
Researchers: Mahdi Tavakoli, Arash Aziminejad, Rajni V. Patel, Mehrdad Moallem
Summary:
Discretization of a stabilizing continuous-time bilateral teleoperation controller for digital implementation may not necessarily lead to stable teleoperation. I studied the stability of master-slave teleoperation under discrete-time bilateral control. Stability regions were determined in the form of conditions involving the sampling period, control gains including the damping introduced by the controller, and environment stiffness. Due to the tradeoff between stability and transparency in bilateral teleoperation, such stability boundaries are of particular importance when the teleoperation system has good transparency.
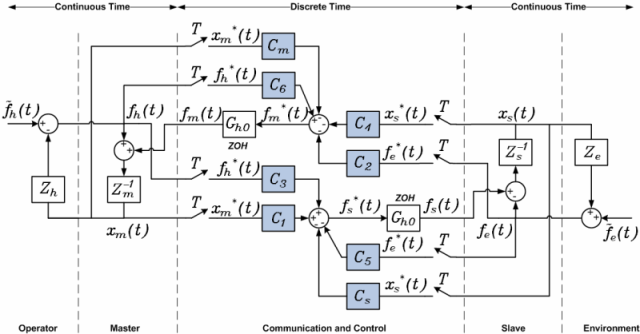
Discrete-time controlled version of the 4-channel teleoperation system.
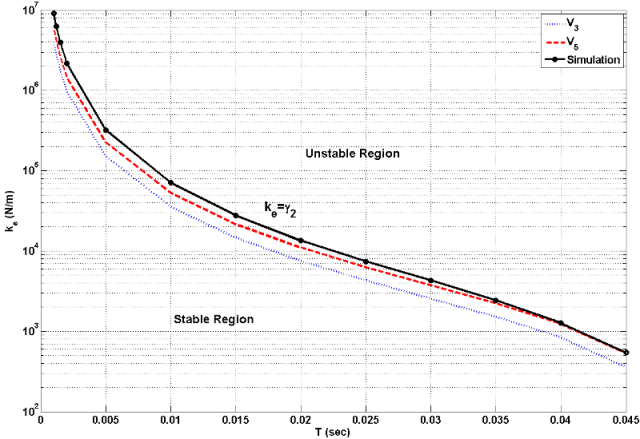
As the sampling period T is increased, the maximum environment stiffness k_e with which a slave robot can stably interact is reduced.